[TipJar] Rock-a-bye-baby
Jan 28
Non-FLOSS, Technology, Tipjar Tipjar, windows No Comments

[Advanced Disclaimer: Use the information in this posting at your risk]
If you want to minimize the amount of electricity used by your computer but dislike shutting down your computer because of the amount of time it need to start it up and open your applications, there is a compromise to be had if your operating system is configured properly to hibernate.
Hibernating an operating system means that all the information in the system memory (RAM to be precise) is written down as a “snapshot image” to the hard disk. The PC hardware is then turned off since the hard disk will not lose its information when powered down. When the machine is turned back on, the booting process of the operating system will look for a store snapshot image and load it back into the system memory. If this is successful, you will have your desktop at the same state as when it was hibernated. The time it needs to resume a hibernated image is relatively small compared to when booting the operating system from scratch (or what is called a cold boot).
All modern operating systems have support for hibernation but not all are enabled by default. To following steps will enable this feature in Windows XP:
- Go to Start->Control Panel->Power Options.
- Go to the “Hibernate” tab and ensure that the “Enable hibernation” check box is ticked. Click OK to dismiss the dialog and apply the change.
WARNING: This will reserve space on the system drive equal to the amount of RAM in your computer. If you have 2GB of RAM, 2GB of hard disk space will be set aside for hibernation. - To hibernate, shutdown the machine but select the hibernate option. The machine will be turned off automatically (if this is properly configured).
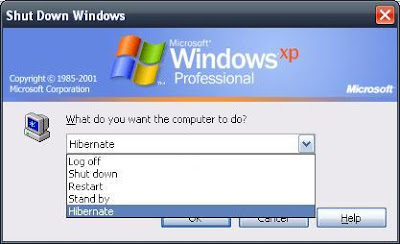
- To resume the hibernated image, turn on the machine. The image will be invalidated after a successful resume.
NOTES:
– Some applications, usually those that have time-bound login sessions, do not like being hibernated.
– The space set aside for the hibernation support is different with the space allocated for the virtual memory.
– If the machine fails to resume or hangs while in the process of resuming, reboot the machine and boot into safe mode (Press F8 after the BIOS screens). Reboot the machine to invalidate the hibernate images and the machine should boot normally after.
 RSS
RSS